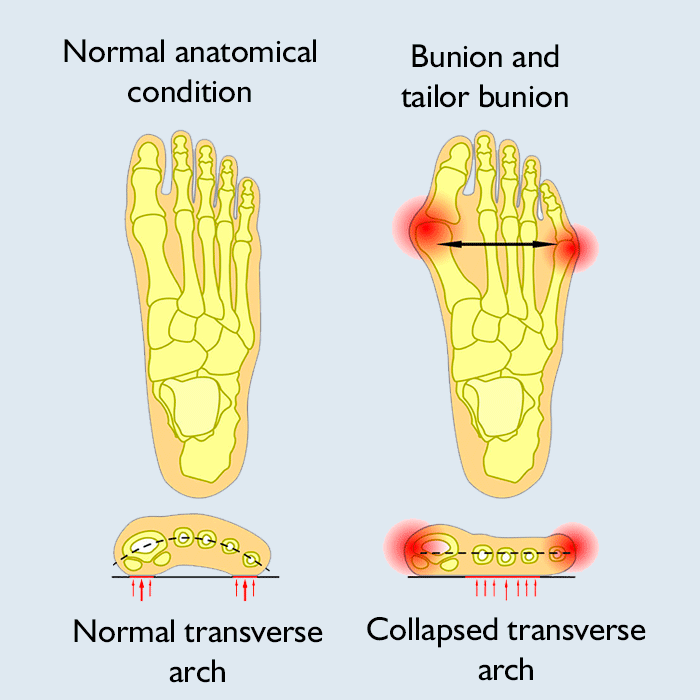
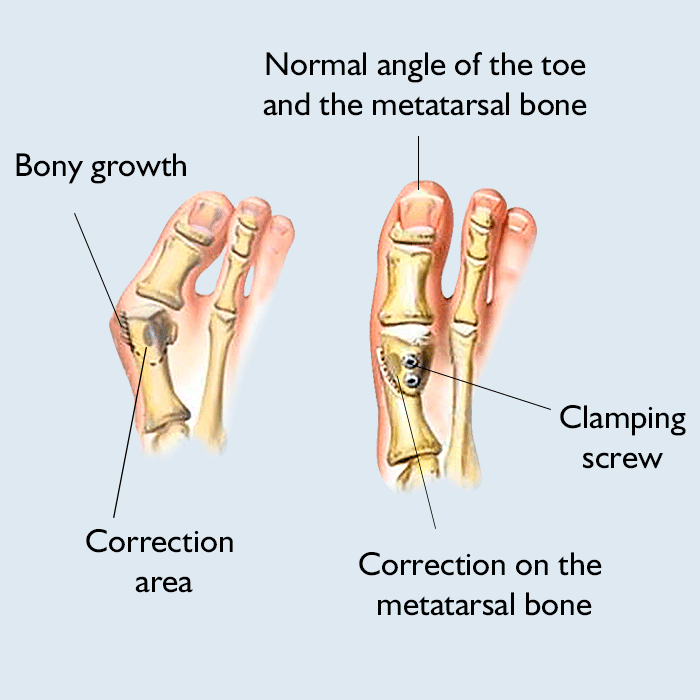
Bunionectomy is a type of orthopedic surgery performed to correct certain deformities of the foot using a variety of techniques. During the pocedure, a bunion is usually excised, and the big toe is restored to its original anatomical position. Sometimes the position of the other toes needs to be adjusted as well.
- Safety First COVID-19
-
Treatments
-
Orthopaedic Surgery
- Arthroscopic knee surgery
- Arthroscopic meniscectomy
- Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) surgery
- Bunion surgery
- Carpal tunnel release
- Chondropathy surgery
- Cubital tunnel release
- Dupuytren’s contracture surgery
- Ganglion Removal
- Hammertoe surgery
- Hip replacement surgery
- Laser Disc Decompression (PLDD)
- Patellar dislocation
- Shoulder surgery
- Total knee replacement
- General Surgery
- Hand surgery
- Gynecological surgery
- ENT Surgery
- Ophthalmic Surgery
- Diagnostics
- Urological surgery
- Proctology
-
Orthopaedic Surgery
- Prices
- Our hospital
- Our Team
- Travel Guide
- Blog
- Contact