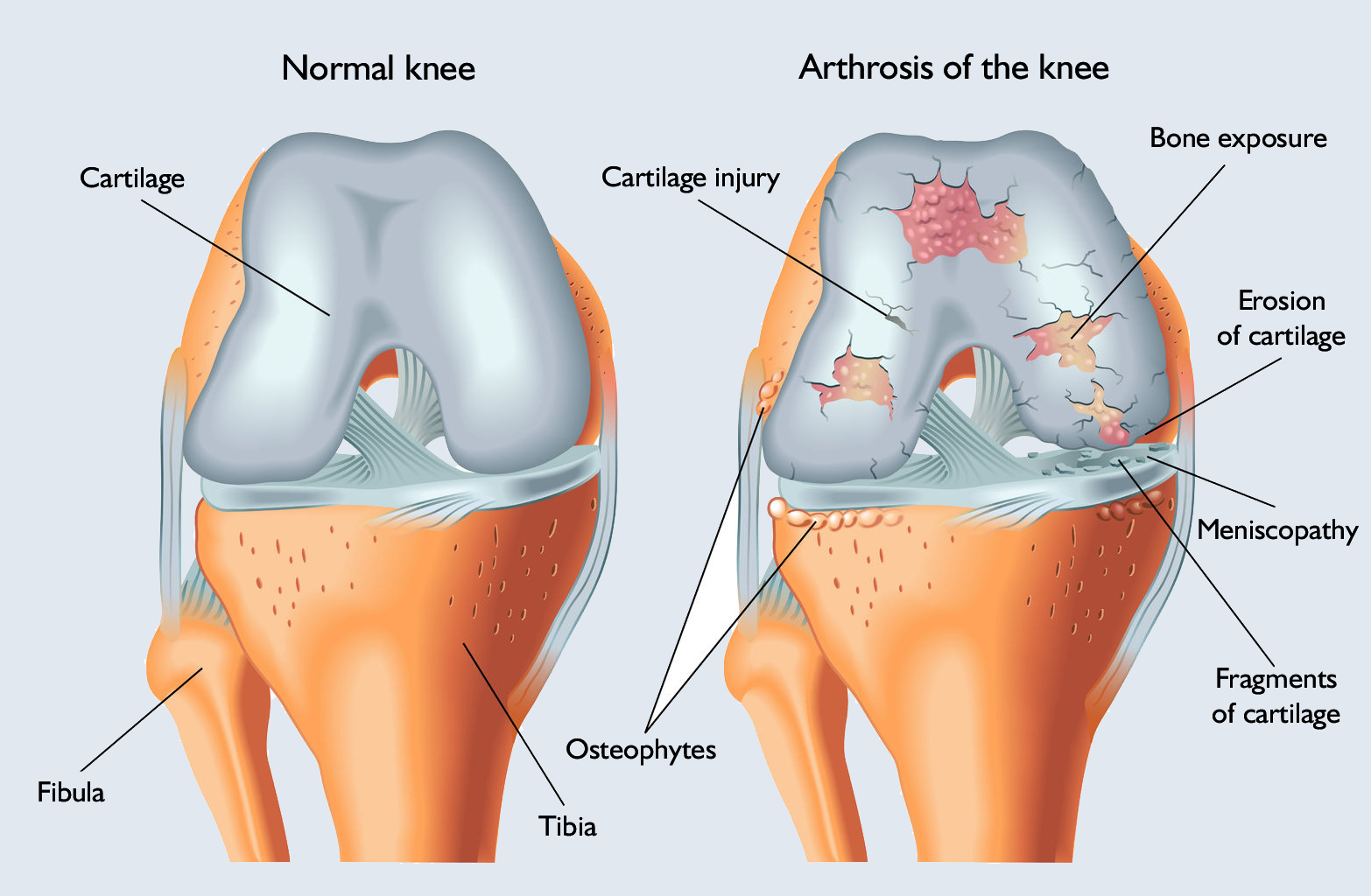
Chondropathy is a degenerative (caused by gradual wear or arthrosis) lesion that affects the entire knee joint and its functioning.
The first thing to suffer structural changes is the cartilage covering the joint: the previously smooth surface becomes cracked.
As the crevasses become deeper, the cartilage falls off in some places. After a while, some parts of the joint may become completely exposed as the cartilage slowly disappears, causing significant pain and loss of function in the joint.