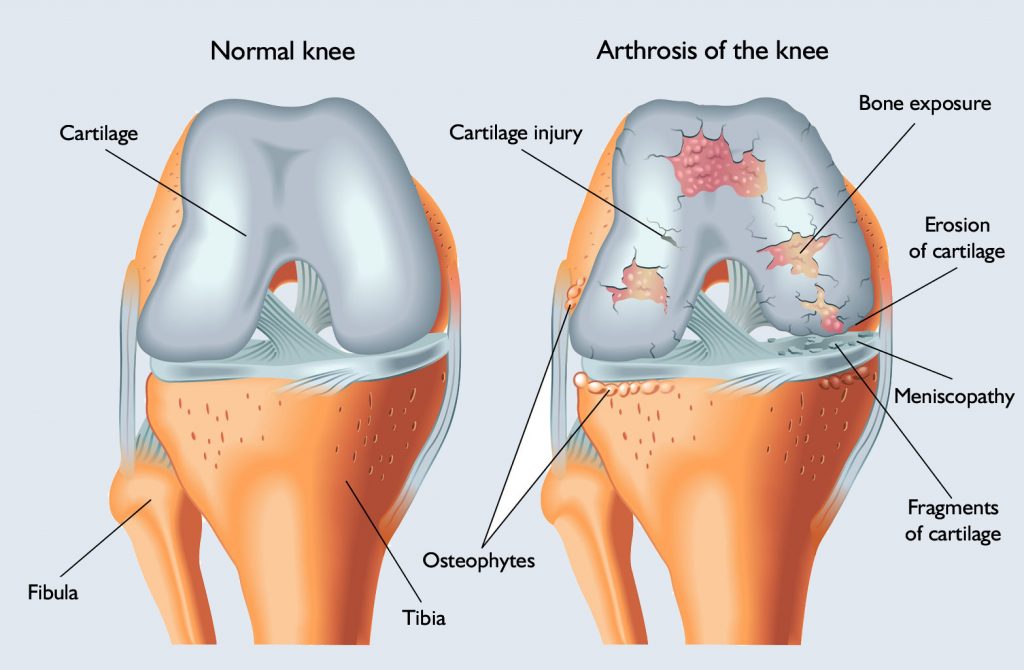
Complaints occur more intense or discreet depending on the magnitude, depth, and location of the lesion. During exercise, pain, cracking, bruising and joint swelling are characteristic. Symptoms may vary; load, exercise are mostly obstructed, but it may even be asymptomatic for a long time.
Typical symptoms are tension, swelling, warming, and fatigue. Usually, complaints cannot be localized to a certain location.