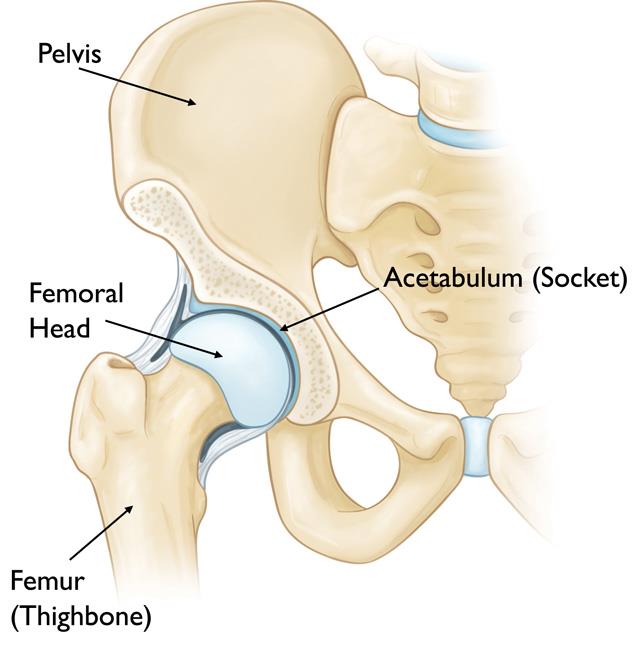
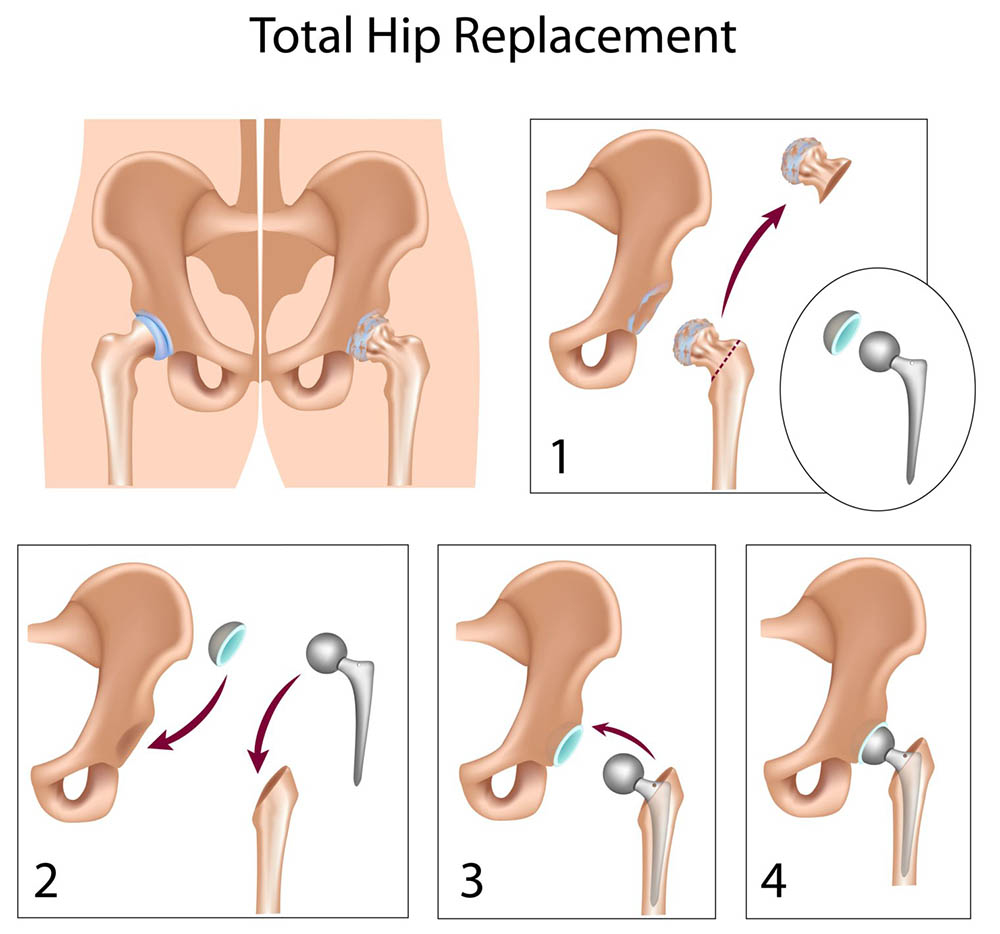
If your doctor has recommended a hip replacement surgery for you, this summary will help you with all the information including the necessary preparation, the complete procedure and the post-operative things to do.
Today prosthetics is the most successful intervention in modern medicine. Hip replacement surgery can result a full and painfree movement of the patient’s hip.