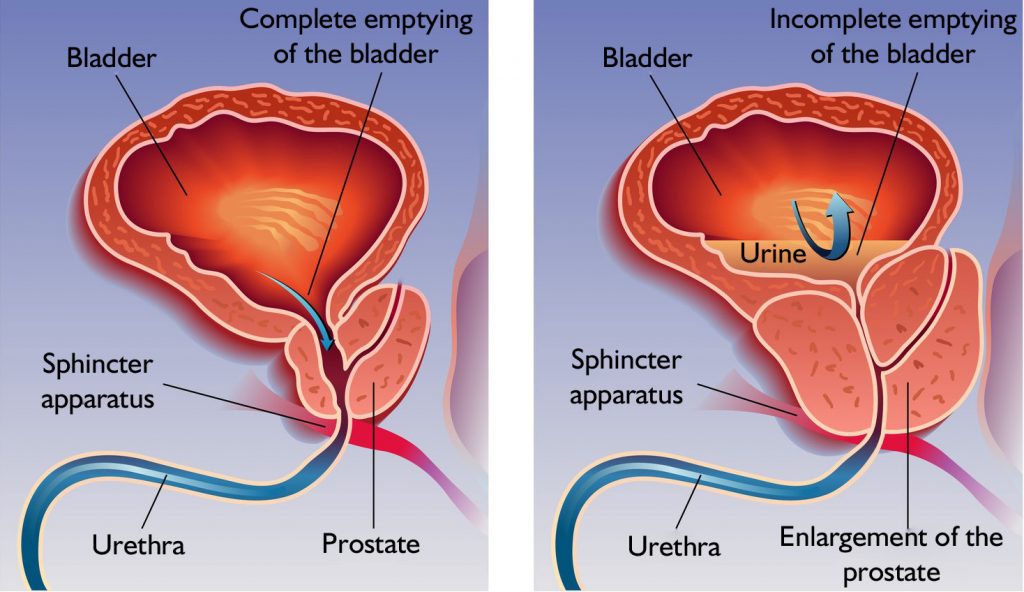
- frequent and sudden urination
- night-time awakening
- difficulty in starting urine
- thin ureteric jet
- intermittent ureteric jet
- incontinence
The causes of its development
At birth, prostate is a pea-sized gland which grows constantly during childhood and reaches its final size at 25 years of age. The cause of non-tumor growth in later years is unknown. Researchers assume that the prostate gland becomes increasingly sensitive to male hormones, for example testosterone.
Apart from the age, family accumulation as genetic tendency can also be a trigger factor.
It is important to know that these symptoms can be caused by other more serious diseases beyond prostate enlargement (cystitis, prostate cancer), and should therefore be directed to a physician in case of such symptoms.
What can cause if you ignore prostate enlargement?
Since the urinary bladder can not completely eradicate during urination, urine begins to bark, bacterial over-infection, bladder inflammation develops. This causes even more frequent, painful, burning-stinging urination, urine may become bloody.
Prostate enlargement frequently may cause bladder stones.
As an acute complication inability to urine may occur when the prostate completely compresses the urinary tract initial stage, making it impossible to urinate, resulting in abrupt abdominal pain. The condition requires immediate treatment, consisting of a fast catheter placement and the urine leaves immediately.
Diagnosis of prostate enlargement
For milder complaints, the urologist decides that regular control is sufficient to establish that the disease does not deteriorate or orders medical treatment.
At the time of blood sampling, the result is general information about the condition of the patient. Determination of a specific protein, prostate antigen (PSA), is essential to investigating prostate diseases. PSA is produced in the body only by the cells of the prostate and its blood concentration is proportional to the size of the prostate.
The abdominal ultrasound test provides an opportunity to evaluate the condition of the kidneys, bladder and prostate.