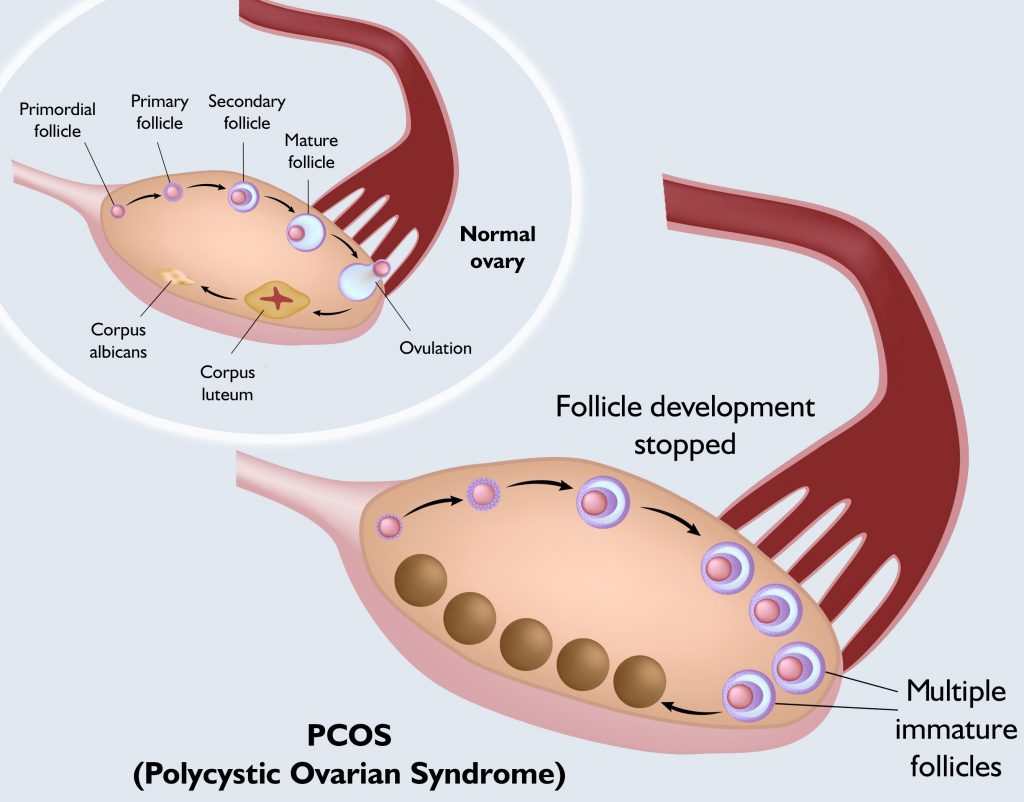
The PCOS is an acronym for polycystic ovarian (ovary) syndrome, which is primarily an ovarian disease, but may also involve several organs. Although the name refers only to the ovary, it requires complex treatment due to its wide range of symptoms. The disease is caused by the formation of a thick, bark-like coating on the ovaries that prevents ovulation. Cysts filled with liquids are formed from the remains of un-cracked follicles.
PCOS is actually a hormonal disorder of the female body, resulting from the male sex hormone, called androgenic excess. This hormone is normally presented in the female body, but excessive amounts of it may produce many unpleasant symptoms.